Chapter 11 Work with Labor Unions
You can’t do it unless you organize.
Samuel Gompers
Only a fool would try to deprive working men and working women of their right to join the union of their choice.
Dwight D. Eisenhower
Unhappy Employees Could Equal Unionization
One afternoon, one of your employees comes to you with some news. She tells you that she has heard talk of employees unionizing if they do not receive pay raises within the next few months. She expresses that the employees are very unhappy and productivity is suffering as a result. She says that employees have already started the unionization process by contacting the National Labor Relations Board and are in the process of proving 30 percent worker interest in unionization. As you mull over this news, you are concerned because the organization has always had a family atmosphere, and a union might change this. You are also concerned about the financial pressures to the organization should the employees unionize and negotiate higher pay. You know you must take action to see that this doesn’t happen. However, you know you and all managers are legally bound by rules relating to unionization, and you need a refresher on what these rules are. You decide to call a meeting first with the CEO and then with managers to discuss strategy and inform them of the legal implications of this process. You feel confident that a resolution can be developed before the unionization happens.
11.1 The Nature of Unions
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
- Be able to discuss the history of labor unions.
- Explain some of the reasons for a decline in union membership over the past sixty years.
- Be able to explain the process of unionization and laws that relate to unionization.
There is a good chance that, at some time in your career, you will join a labor union. The purpose of this chapter is to give you some background about unions. Oftentimes, depending on your union involvement, you may have to use a number of human relations skills you have gained so far from reading this book. For example, the ability to work in a team and handle conflict are all aspects you may experience as a union member—or a member of any organization. A labor union, or union, is defined as workers banding together to meet common goals, such as better pay, benefits, or promotion rules. In the United States, 11.9 percent of American workers belong to a union, down from 20.1 percent in 1983.“Union Members: 2010,” Bureau of Labor Statistics, US Department of Labor, news release, January 21, 2011, accessed April 4, 2011, http://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/union2.pdf. In this section, we will discuss the history of unions, reasons for decline in union membership, union labor laws, and the process employees go through to form a union. First, however, we should discuss some of the reasons why people join unions.
People may feel their economic needs are not being met with their current wages and benefits and believe that a union can help them receive better economic prospects. Fairness in the workplace is another reason why people join unions. They may feel that scheduling, vacation time, transfers, and promotions are not given fairly and feel that a union can help eliminate some of the unfairness associated with these processes. Let’s discuss some basic information about unions before we discuss the unionization process.
History and Organization of Unions
Trade unions were developed in Europe during the Industrial Revolution, when employees had little skill and thus the entirety of power was shifted to the employer. When this power shifted, many employees were treated unfairly and underpaid. In the United States, unionization increased with the building of railroads in the late 1860s. Wages in the railroad industry were low and the threat of injury or death was high, as was the case in many manufacturing facilities with little or no safety laws and regulations in place. As a result, the Brotherhood of Locomotive Engineers and several other brotherhoods (focused on specific tasks only, such as conductors and brakemen) were formed to protect workers’ rights, although many workers were fired because of their membership.
Labor Union AFL-CIO Perspective
A video from the AFL-CIO shows a history of labor unions, from its perspective.
The first local unions in the United States were formed in the eighteenth century, in the form of the National Labor Union (NLU).
The National Labor Union, formed in 1866, paved the way for other labor organizations. The goal of the NLU was to form a national labor federation that could lobby government for labor reforms on behalf of the labor organizations. Its main focus was to limit the workday to eight hours. While the NLU garnered many supporters, it excluded Chinese workers and only made some attempts to defend the rights of African Americans and female workers. The NLU can be credited with the eight-hour workday, which was passed in 1862. Because of a focus on government reform rather than collective bargaining, many workers joined the Knights of Labor in the 1880s.
The Knights of Labor started as a fraternal organization, and when the NLU dissolved, the Knights grew in popularity as the labor union of choice. The Knights promoted the social and cultural spirit of the worker better than the NLU had. It originally grew as a labor union for coal miners but also covered several other types of industries. The Knights of Labor initiated strikes that were successful in increasing pay and benefits. When this occurred, membership increased. After only a few years, though, membership declined because of unsuccessful strikes, which were a result of a too autocratic structure, lack of organization, and poor management. Disagreements between members within the organization also caused its demise.
The American Federation of Labor (AFL) was formed in 1886, mostly by people who wanted to see a change from the Knights of Labor. The focus was on higher wages and job security. Infighting among union members was minimized, creating a strong organization that still exists today: in the 1930s, the Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) was formed as a result of political differences in the AFL. In 1955, the two unions joined together to form the AFL-CIO.
Currently, the AFL-CIO is the largest federation of unions in the United States and is made up of fifty-six national and international unions. The goal of the AFL-CIO isn’t to negotiate specific contracts for employees but rather to support the efforts of local unions throughout the country.
Figure 11.1 The Complicated Structure of AFL-CIO

Source: AFL-CIO.
Currently in the United States, there are two main national labor unions that oversee several industry-specific local unions. There are also numerous independent national and international unions that are not affiliated with either national union:
- AFL-CIO: local unions include Airline Pilots Association, American Federation of Government Employees, Associated Actors of America, and Federation of Professional Athletes
- CTW (Change to Win Federation): includes the Teamsters, Service Employees International Union, United Farm Workers of America, and United Food and Commercial Workers
- Independent unions: Directors Guild of America, Fraternal Order of Police, Independent Pilots Association, Major League Baseball Players Association
The national union plays an important role in legislative changes, while the local unions focus on collective bargaining agreements and other labor concerns specific to the area. Every local union has a union steward who represents the interests of union members. Normally, union stewards are elected by their peers.
A national union, besides focusing on legislative changes, also does the following:
- Lobbies in government for worker rights laws
- Resolves disputes between unions
- Helps organize national protests
- Works with allied organizations and sponsors various programs for the support of unions
For example, in 2011, the national Teamsters union organized demonstrations in eleven states to protest the closing of an Ontario, California, parts distribution center. Meanwhile, Teamster Local 495 protested at the Ontario plant.“Teamsters Escalate BMW Protests across America,” PR Newswire, August 2, 2011, accessed August 15, 2011, http://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/teamsters-escalate-bmw-protests-across-america-126619168.html.
Current Union Challenges
The labor movement is currently experiencing several challenges, including a decrease in union membership, globalization, and employers’ focus on maintaining nonunion status. As mentioned in the opening of this section, the United States has seen a steady decline of union membership since the 1950s. In the 1950s, 36 percent of all workers were unionized,Gerald Friedman, “Labor Unions in the United States,” Economic History Association, February 2, 2010, accessed April 4, 2011, http://eh.net/encyclopedia/article/friedman.unions.us. as opposed to just over 11 percent today.
Claude Fischer, a researcher from University of California Berkeley, believes the shift is cultural. His research says the decline is a result of American workers preferring individualism as opposed to collectivism.Claude Fischer, “Why Has Union Membership Declined?” Economist’s View, September 11, 2010, accessed April 11, 2011, http://economistsview.typepad.com/economistsview/2010/09/why-has-union-membership-declined.html. Other research says the decline of unions is a result of globalization and the fact that many jobs that used to be unionized in the manufacturing arena have now moved overseas. Other reasoning points to management and that its unwillingness to work with unions has caused the decline in membership. Others suggest that unions are on the decline because of themselves. Past corruption, negative publicity, and hard-line tactics have made joining a union less favorable.
To fully understand unions, it is important to recognize the global aspect of unions. Statistics on a worldwide scale show unions in all countries declining but still healthy in some countries. For example, in eight of the twenty-seven European Union member states, more than half the working population is part of a union. In fact, in the most populated countries, unionization rates are still at three times the unionization rate of the United States.Federation of European Employers, “Trade Unions across Europe,” accessed April 4, 2011, http://www.fedee.com/tradeunions.html. Italy has a unionization rate of 30 percent of all workers, while the UK has 29 percent, and Germany has a unionization rate of 27 percent.
In March 2011, Wisconsin governor Scott Walker proposed limiting the collective bargaining rights of state workers to save a flailing budget. Some called this move “union busting” and said this type of act is illegal, as it takes away the basic rights of workers. The governor defended his position by saying there is no other choice, since the state is in a budget crisis. Other states such as Ohio are considering similar measures. Whatever happens, there is a clear shift for unions today.
Globalization is also a challenge in labor organizations today. As more and more goods and services are produced overseas, unions lose not only membership but also union values in the stronghold of worker culture. As globalization has increased, unions have continued to demand more governmental control but have been only somewhat successful in these attempts. For example, free trade agreements such as the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) have made it easier and more lucrative for companies to manufacture goods overseas. For example, La-Z-Boy and Whirlpool closed production facilities in Dayton and Cleveland, Ohio, and built new factories in Mexico to take advantage of cheaper labor and less stringent environmental standards. Globalization creates options for companies to produce goods wherever they think is best to produce them. As a result, unions are fighting the globalization trend to try and keep jobs in the United States.
There are a number of reasons why companies do not want unions in their organizations, which we will discuss in greater detail later. One of the main reasons, however, is increased cost and less management control. As a result, companies are on a quest to maintain a union-free work environment. In doing so, they try to provide higher wages and benefits so workers do not feel compelled to join a union. Companies that want to stay union free constantly monitor their retention strategies and policies.
Labor Union Laws
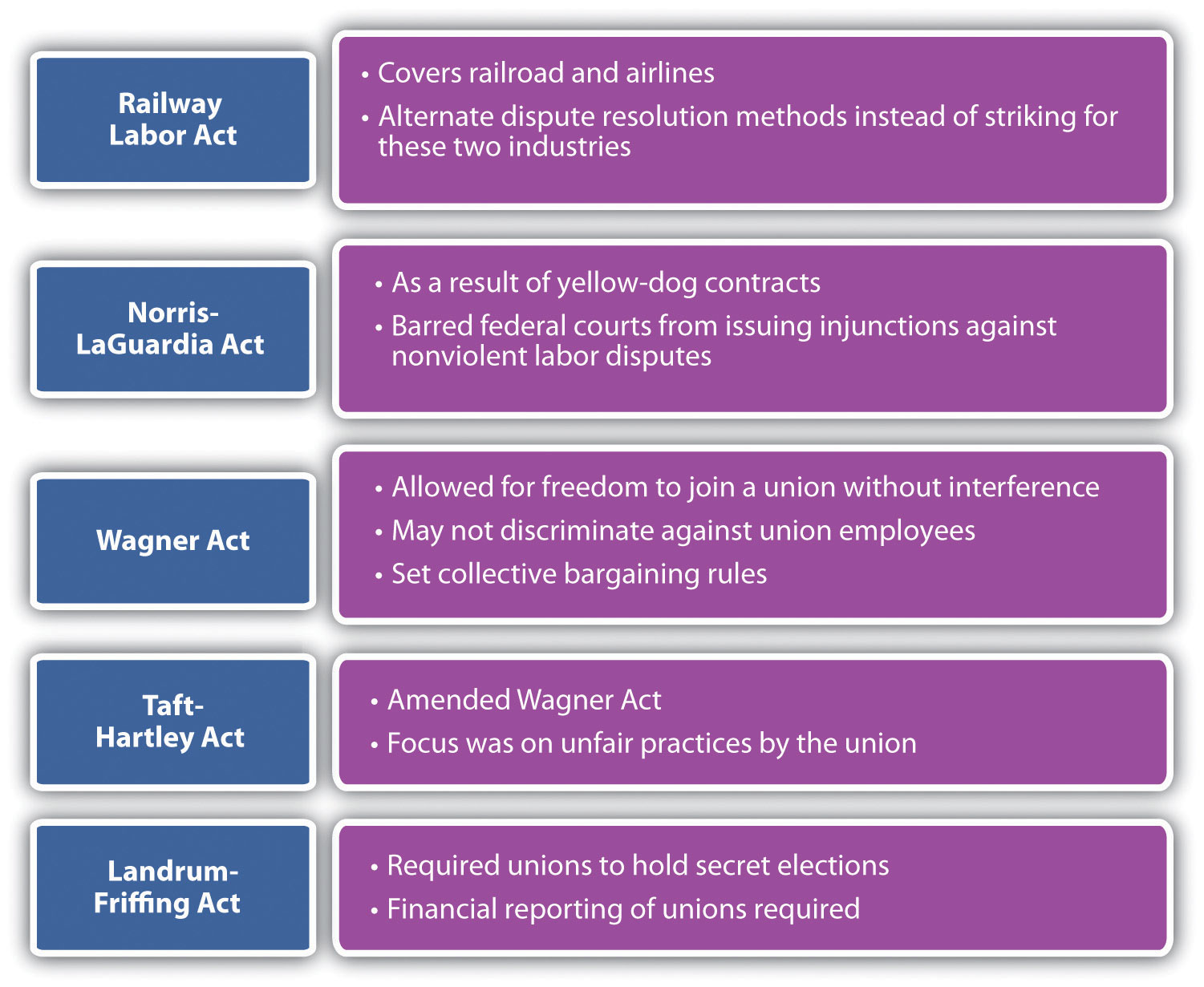
The Railway Labor Act (RLA) of 1926 originally applied to railroads and in 1936 was amended to cover airlines. The act received support from both management and unions. The goal of the act is to ensure no disruption of interstate commerce. The main provisions of the act include alternate dispute resolution, arbitration, and mediation to resolve labor disputes. Any dispute must be resolved in this manner before a strike can happen. The RLA is administered by the National Mediation Board (NMB), a federal agency, and outlines very specific and detailed processes for dispute resolution in these industries.
The Norris-LaGuardia Act of 1932 (also known as the anti-injunction bill) barred federal courts from issuing injunctions (a court order that requires a party to do something or refrain from doing something) against nonviolent labor disputes and barred employers from interfering with workers joining a union. The act was a result of common yellow-dog contracts, in which a worker agreed not to join a union before accepting a job. The Norris-LaGuardia Act made yellow-dog contracts unenforceable in courts and established that employees were free to join unions without employer interference.
In 1935, the Wagner Act (sometimes called the National Labor Relations Act) was passed, changing the way employers can react to several aspects of unions. The Wagner Act had a few main aspects:
- Employers must allow freedom of association and organization and cannot interfere with, restrain or coerce employees who form a union.
- Employers may not discriminate against employees who form or are part of a union or those who file charges.
- An employer must bargain collectively with representation of a union.
The National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) oversees this act, handling any complaints that may arise from the act. For example, in April 2011, the NLRB worked with employees at Ozburn-Hessey Logistics in Tennessee after they had been fired because of their involvement in forming a union. The company was also accused of interrogating employees about their union activities and threatened employees with loss of benefits should they form a union. The NLRB utilized their attorney to fight on behalf of the employees, and a federal judge ordered the company to rehire the fired employees and also to desist in other antiunion activities.“Federal Judge Orders Employer to Reinstate Three Memphis Warehouse Workers and Stop Threatening Union Supporters While Case Proceeds at NLRB,” Office of Public Affairs, National Labor Relations Board, news release, April 7, 2011, accessed April 7, 2011, http://www.nlrb.gov/news/federal-judge-orders-employer-reinstate-three-memphis-warehouse-workers- and-stop-threatening-un.
The Taft-Hartley Act also had major implications for unions. Passed in 1947, Taft-Hartley amended the Wagner Act. The act was introduced because of the upsurge of strikes during this time period. While the Wagner Act addressed unfair labor practices on the part of the company, the Taft-Hartley Act focused on unfair acts by the unions. For example, it outlawed strikes that were not authorized by the union, called wildcat strikes. It also prohibited secondary actions (or secondary boycotts) in which one union goes on strike in sympathy for another union. The act allowed the executive branch of the federal government to disallow a strike should the strike affect national health or security. One of the most famous injunctions was made by President Ronald Reagan in 1981. Air traffic controllers had been off the job for two days despite their no-strike oath, and Reagan ordered all of them (over eleven thousand) discharged because they violated this federal law.
Figure 11.2

The Taft-Hartley Act prevents certain types of strikes, even in unionized companies.
© Thinkstock
The Landrum Griffin Act, also known as the Labor Management Reporting and Disclosure (LMRDA) Act, was passed in 1959. This act required unions to hold secret elections, required unions to submit their annual financial reports to the US Department of Labor, and created standards governing expulsion of a member from a union. This act was created because of racketeering charges and corruption charges by unions. In fact, investigations of the Teamsters union found they were linked to organized crime, and the Teamsters were banned from the AFL-CIO. The goal of this act was to regulate the internal functioning of unions and to combat abuse of union members by union leaders.
Figure 11.3 Major Acts Regarding Unions, at a Glance
The Unionization Process
There are one of two ways in which a unionization process can begin. First, the union may contact several employees and discuss the possibility of a union, or employees may contact a union on their own. The union will then help employees gather signatures to show that the employees want to be part of a union. To hold an election, the union must show signatures from over 30 percent of the employees of the organization.
Figure 11.4 The Unionization Process
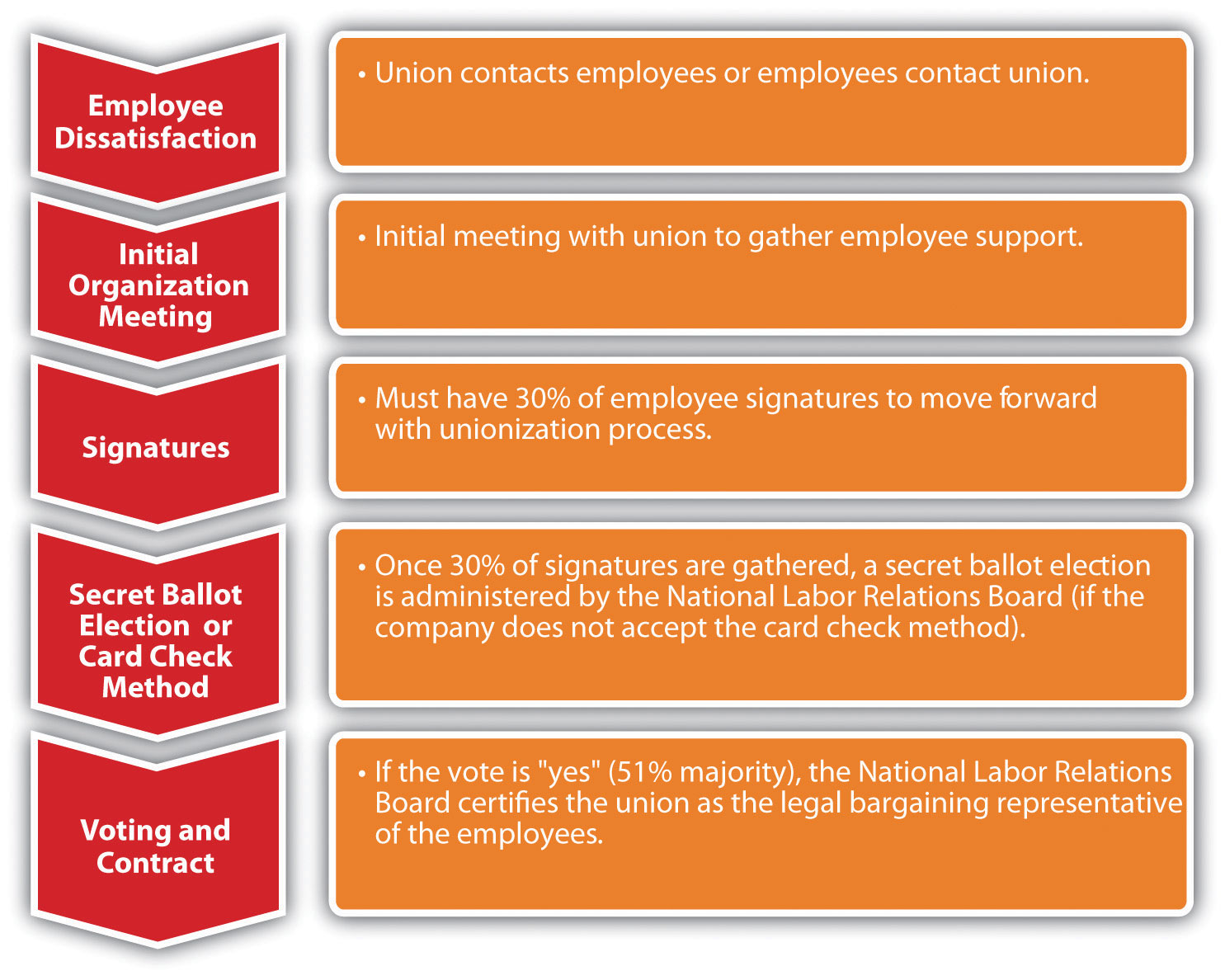
Once the signatures are gathered, the National Labor Relations Board is petitioned to move forward with a secret-ballot election. An alternative to the secret-ballot election is the card check method, in which the union organizer provides the company with authorization cards signed by a simple majority (half plus one). The employer can accept the cards as proof that the employees desire a union in their organization. The NLRB then certifies the union as the employees’ collective bargaining representative.
If the organization does not accept the card check method as authorization for a union, the second option is via a secret ballot. Before this method is used, a petition must be filed by the NLRB, and an election is usually held two months after the petition is filed. In essence, the employees vote whether to unionize or not, and there must be a simple majority (half plus one). The NLRB is responsible for election logistics and counting of ballots. Observers from all parties can be present during the counting of votes. Once votes are counted, a decision on unionization occurs, and at that time, the collective bargaining process begins.
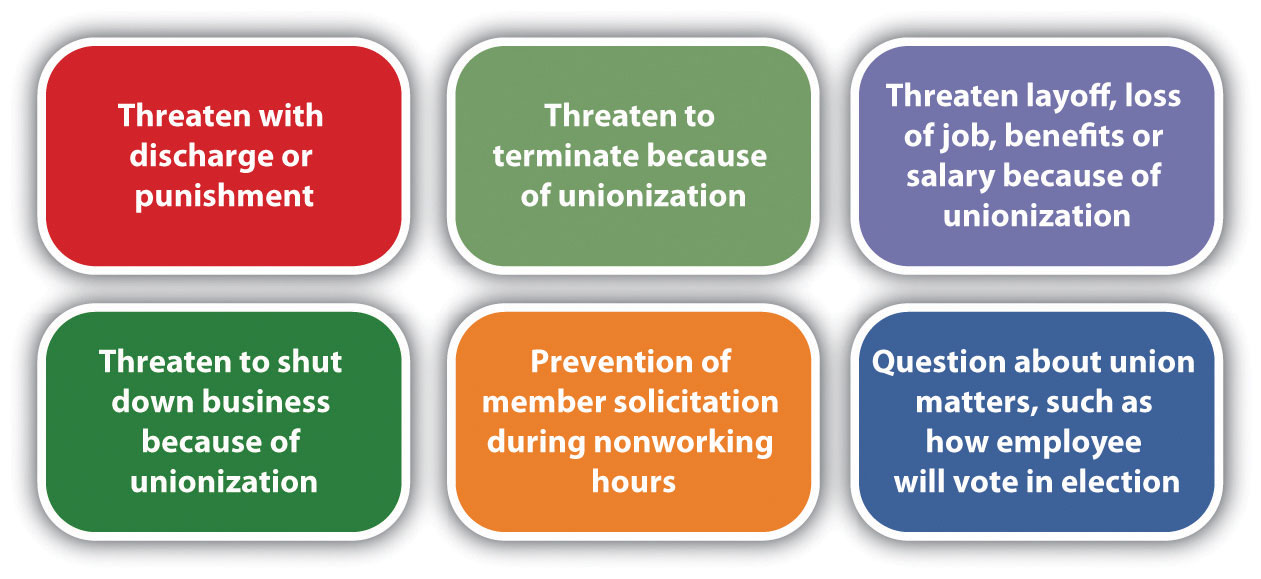
Once the NLRB is involved, there are many limits as to what the employer can say or do during the process to prevent unionization of the organization. It is advisable for HR and management to be educated on what can legally and illegally be said during this process. It is illegal to threaten or intimidate employees if they are discussing a union. You cannot threaten job, pay, or benefits loss as a result of forming a union. Figure 11.5 “Things That Shouldn’t Be Said to Employees during a Unionization Process” includes information on what should legally be avoided if employees are considering unionization.
Figure 11.5 Things That Shouldn’t Be Said to Employees during a Unionization Process
Obviously, it is in the best interest of the union to have as many members as possible. Because of this, unions may use many tactics during the organizing process. For example, many unions are also politically involved and support candidates who they feel best represent labor. They provide training to organizers and sometimes even encourage union supporters to apply for jobs in nonunion environments to actively work to unionize other employees when they are hired. This practice is called union salting. Unions, especially on the national level, can be involved in corporate campaigns that boycott certain products or companies because of their labor practices. The United Food and Commercial Workers (UFCW), for example, has a “Wake Up Walmart Campaign” that targets the labor practices of this organization.
Strategies Companies Use to Avoid Unionization
Most organizations feel the constraints of having a union organization are too great. It affects the cost to the organization and operation efficiency. Collective bargaining at times can put management at odds with its employees and cost more to produce products and services. Ideally, companies will provide safe working conditions, fair pay, and benefits so the employees do not feel they need to form a union.
When a union vote may occur, most organizations will develop specific strategies to encourage employees to vote “no” for the union. Some of the arguments that might be used include talking with the employee and mentioning the following:
- Union dues are costly.
- Employees could be forced to go on strike.
- Employees and management may no longer be able to discuss matters informally and individually.
- Unionization can create more bureaucracy within the company.
- Individual issues may not be discussed.
- Many decisions within a union, such as vacation time, are based on seniority only.
Organizations such as Change to Win are in the process of trying to increase union membership. This organization has four affiliated unions, with a goal to strengthen the labor movement. Teamsters, United Food and Commercial Workers, United Farm Workers, and Service Employees International Union are all unions affiliated with this organization.Change to Win website, accessed April 7, 2011, http://www.changetowin.org. The next few years will be telling as to the fate of unions in today’s organizations.
The Impact of Unions on Organizations
You may wonder why organizations are opposed to unions. As we have mentioned, since union workers do receive higher wages, this can be a negative impact on the organization. Unionization also impacts the ability of managers to make certain decisions and limits their freedom when working with employees. For example, if an employee is constantly late to work, the union contract will specify how to discipline in this situation, resulting in little management freedom to handle this situation on a case-by-case basis. In 2010, for example, the Art Institute of Seattle faculty filed signatures and voted on unionization.“Union Push in For-Profit Higher Ed,” Inside Higher Ed, May 24, 2010, accessed August 15, 2011, http://www.insidehighered.com/news/2010/05/24/union. Some of the major issues were scheduling issues and office space, not necessarily pay and benefits. While the particular National Labor Relations Board vote was no to unionization, a yes vote could have given less freedom to management in scheduling, since scheduling would be based on collective bargaining contracts. Another concern about unionization for management is the ability to promote workers. A union contract may stipulate certain terms (such as seniority) for promotion, which means the manager has less control over the employees he or she can promote.
Section 11.2 “Collective Bargaining” and Section 11.3 “Grievance Process” discuss the collective bargaining and grievance processes.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Union membership in the United States has been slowly declining. Today, union membership consists of about 11.9 percent of the workforce, while in 1983 it consisted of 20 percent of the workforce.
- The reasons for decline are varied, depending on whom you ask. Some say the moving of jobs overseas is the reason for the decline, while others say unions’ hard-line tactics put them out of favor.
- Besides declining membership, union challenges today include globalization and companies’ wanting a union-free workplace.
- The United States began its first labor movement in the 1800s. This was a result of low wages, no vacation time, safety issues, and other issues.
- Many labor organizations have disappeared, but the American Federation of Labor (AFL) still exists today, although it merged with the Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) and is now known as the AFL-CIO. It is the largest labor union and represents local labor unions in a variety of industries.
- The United States has a low number of union members compared with other countries. Much of Europe, for example, has over 30 percent of their workforce in labor unions, while in some countries as much as 50 percent of the workforce are members of a labor union.
- Legislation has been created over time to support both labor unions and the companies who have labor unions. The Railway Labor Act applies to airlines and railroads and stipulates that employees may not strike until they have gone through an extensive dispute resolution process. The Norris-LaGuardia Act made yellow-dog contracts illegal and barred courts from issuing injunctions.
- The Wagner Act was created to protect employees from retaliation should they join a union. The Taft-Hartley Act was developed to protect companies from unfair labor practices by unions.
- The National Labor Relations Board is the overseeing body for labor unions, and it handles disputes between companies as well as facilitates the process of new labor unions in the developing stages. Its job is to enforce both the Wagner Act and the Taft-Hartley Act.
- The Landrum Griffin Act was created in 1959 to combat corruption in labor unions during this time period.
- To form a union, the organizer must have signatures from 30 percent of the employees. If this occurs, the National Labor Relations Board will facilitate a card check to determine more than 50 percent of the workforce at that company is in agreement with union representation. If the company does not accept this, then the NLRB holds secret elections to determine if the employees will be unionized. A collective bargaining agreement is put into place if the vote is yes.
- Companies prefer to not have unions in their organizations because it affects costs and operational productivity. Companies will usually try to prevent a union from organizing in their workplace.
- Managers are impacted when a company does unionize. For example, management rights are affected, and everything must be guided by the contract instead of management prerogative.
EXERCISES
- Visit the National Labor Relations Board website. View the “weekly case summary” and discuss it in at least two paragraphs, stating your opinion on this case.
- Do you agree with unionization within organizations? Why or why not? List the advantages and disadvantages of unions to the employee and the company.
11.2 Collective Bargaining
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
- Be able to describe the process of collective bargaining.
- Understand the types of bargaining issues and the rights of management.
- Discuss some strategies if you become part of a union.
When employees of an organization vote to unionize, the process for collective bargaining begins. Collective bargaining is the process of negotiations between the company and representatives of the union. You probably remember our discussion on negotiations in Chapter 9 “Handle Conflict and Negotiation”. Many of the tips in that chapter can help you should you ever be in a position to negotiate on behalf of a union or management.
The goal is for management and the union to reach a contract agreement, which is put into place for a specified period of time. Once this time is up, a new contract is negotiated. In this section, we will discuss the components of the collective bargaining agreement.
The Process of Collective Bargaining
In any bargaining agreement, certain management rights are not negotiable, including the right to manage and operate the business, hire, promote, or discharge employees. However, in the negotiated agreement there may be a process outlined by the union for how these processes should work. Management rights also include the ability of the organization to direct the work of the employees and to establish operational policies.
Another important point in the collective bargaining process is the aspect of union security. Obviously, it is in the union’s best interest to collect dues from members and recruit as many new members as possible. In the contract, a checkoff provision may be negotiated. This provision occurs when the employer, on behalf of the union, automatically deducts dues from union members’ paychecks. This ensures that a steady stream of dues is paid to the union.
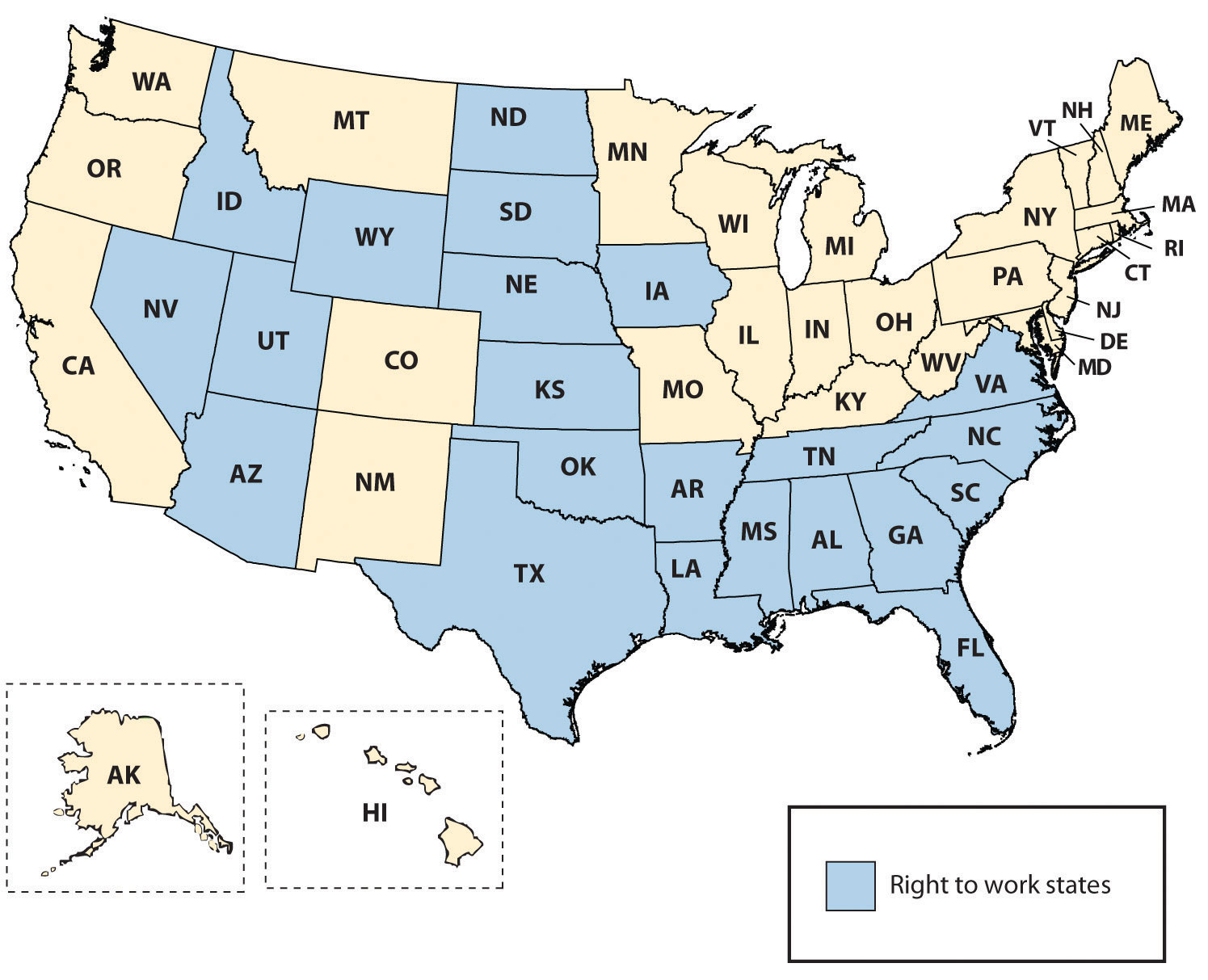
To recruit new members, the union may require something called a union shop. A union shoprequires a person to join the union within a certain time period of joining the organization. In right-to-work states a union shop may be illegal. Twenty-two states have passed right-to-work laws, as you can see in Figure 11.6 “Map of Right-to-Work States”. These laws prohibit a requirement to join a union or pay dues and fees to a union. To get around these laws, agency shops were created. An agency shop is similar to a union shop in that workers do not have to join the union but still must pay union dues. Agency shop union fees are known as agency fees and may be illegal in right-to-work states. A closed shop used to be a mechanism for a steady flow of membership. In this arrangement, a person must be a union member to be hired. This, however, was made illegal under the Taft-Hartley Act. According to a study by CNBC, all twenty-two right-to-work states are in the top twenty-five states for having the best workforces.“Best Workforces Are in Right to Work States,” Redstate, June 30, 2011, accessed August 14, 2011, http://www.redstate.com/laborunionreport/2011/06/30/best-workforces-are-in-right-to-work-states-survey-finds/. However, according to the AFL-CIO, the average worker in a right-to-work state makes $5,333 less per year than other workers.“Right to Work for Less,” AFL-CIO, accessed August 14, 2011, http://www.aflcio.org/Legislation-and-Politics/State-Legislative-Battles/Ongoing-State-Legislative-Attacks/Right-to-Work-for-Less.
Figure 11.6 Map of Right-to-Work States
In a collective bargaining process, both parties are legally bound to bargain in good faith. This means they have a mutual obligation to participate actively in the deliberations and indicate a desire to find a basis for agreement. There are three main classification of bargaining topics: mandatory, permissive, and illegal. Wages, health and safety, management rights, work conditions, and benefits fall into the mandatory category. Permissive topics are those that are not required but may be brought up during the process. An example might include the requirement of drug testing for candidates or the required tools that must be provided to the employee to perform the job, such as a cellular phone or computer. It is important to note that while management is not required by labor laws to bargain on these issues, refusing to do so could affect employee morale. We can also classify bargaining issues as illegal topics, which obviously cannot be discussed. These types of illegal issues may be of a discriminatory nature or anything that would be considered illegal outside the agreement.
Examples of Bargaining Topics
- Pay rate and structure
- Health benefits
- Incentive programs
- Job classification
- Performance assessment procedure
- Vacation time and sick leave
- Health plans
- Layoff procedures
- Seniority
- Training process
- Severance pay
- Tools provided to employees
- Process for new applicants
The collective bargaining process has five main steps; we will discuss each of these steps next. The first step is the preparation of both parties. The negotiation team should consist of individuals with knowledge of the organization and the skills to be an effective negotiator. An understanding of the working conditions and dissatisfaction with working conditions is an important part of this preparation step. Establishing objectives for the negotiation and reviewing the old contract are key components to this step. Both sides should also prepare and anticipate demands, to better prepare for compromises.
Figure 11.7 Steps in Collective Bargaining
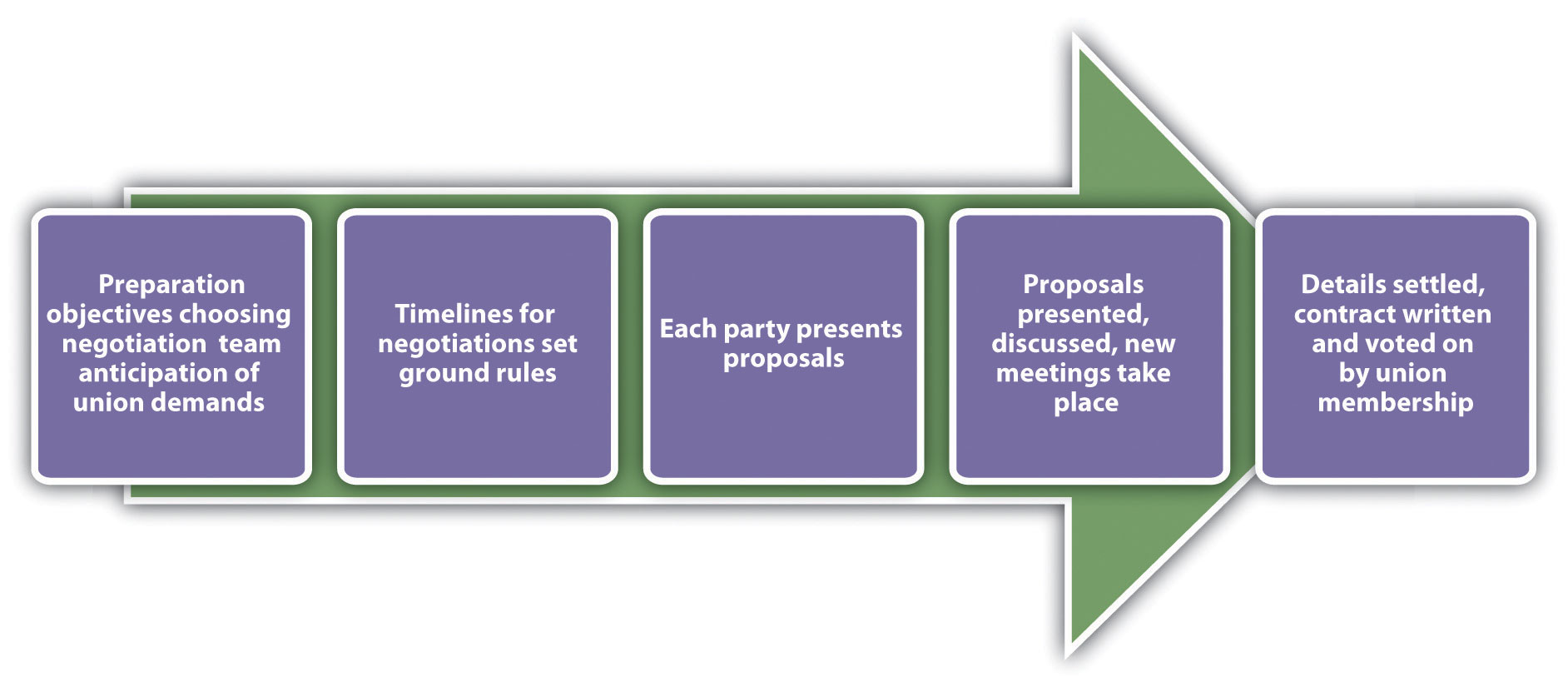
The second step of the process involves both parties agreeing on how the timelines will be set for the negotiations. In addition, setting ground rules for how the negotiation will occur is an important step, as it lays the foundation for the work to come.
In the third step, each party comes to the table with proposals. It will likely involve initial opening statements and options that exist to resolve any situations that exist. The key to a successful proposal is to come to the table with a “let’s make this work” attitude. An initial discussion is had and then each party generally goes back to determine which requests it can honor and which it can’t. At this point, another meeting is generally set up to continue further discussion.
Once the group comes to an agreement or settlement (which may take many months and proposals), a new contract is written and the union members vote on whether to accept the agreement. If the union doesn’t agree, then the process begins all over again.
Ramifications of a Bargaining Impasse
When the two parties are unable to reach consensus on the collective bargaining agreement, this is called a bargaining impasse. Various kinds of strikes are used to show the displeasure of workers regarding a bargaining impasse. An economic strike is a strike stemming from unhappiness about the economic conditions during contract negotiations. For example, 45,000 Verizon workers rallied in the summer of 2011 when contract negotiations failed.Dan Goldberg, “Verizon Strike Could Last Months,” New Jersey News, August 7, 2011, accessed August 15, 2011, http://www.nj.com/news/index.ssf/2011/08/verizon_workers_outline_differ.html. The two unions, Communications Workers of America and the International Brotherhood of Electric Workers, claim that the new contract is unfair, as it asks Verizon workers to contribute more to health plans, and the company is also looking to freeze pensions at the end of the year and reduce sick time.Dan Goldberg, “Verizon Strike Could Last Months,” New Jersey News, August 7, 2011, accessed August 15, 2011, http://www.nj.com/news/index.ssf/2011/08/verizon_workers_outline_differ.html. Verizon says the telecommunications business is changing, and it cannot afford these expenses. An unfair labor practices strike can happen during negotiations. The goal of an unfair labor practices strike is to get the organization to cease committing what the union believes to be an unfair labor practice. A bargaining impasse could mean the union goes on strike or a lockout occurs. The goal of a lockout, which prevents workers from working, is to put pressure on the union to accept the contract. A lockout can only be legally conducted when the existing collective bargaining agreement has expired and there is truly an impasse in contract negotiations. In summer 2011, the National Basketball Association locked out players when the collective bargaining agreement expired, jeopardizing the 2011–12 seasonSteve Kyler, “Division among Owners?” HoopsWorld, August 8, 2011, accessed August 15, 2011, http://www.hoopsworld.com/nba-am-division-among-nba-owners/. while putting pressure on the players to accept the agreement. Similarly, the goal of a strike is to put pressure on the organization to accept the proposed contract. Some organizations will impose a lockout if workers engage in slowdowns, an intentional reduction in productivity. Some unions will engage in a slowdown instead of a strike, because the workers still earn pay, while in a strike they do not. A sick-out is when members of a union call in sick, which may be illegal since they are using allotted time, while a walk-out is an unannounced refusal to perform work. However, this type of tactic may be illegal if the conduct is irresponsible or indefensible, according to a judge. Jurisdictional strikesare used to put pressure on an employer to assign work to members of one union versus another (if there are two unions within the same organization) or to put pressure on management to recognize one union representation when it currently recognizes another. The goal of a sick-out strike is to show the organization how unproductive the company would be if the workers did go on strike. As mentioned under the Taft-Hartley Act, wildcat strikes are illegal, as they are not authorized by the union and usually violate a collective bargaining agreement. Sympathy strikes are work stoppages by other unions designed to show support for the union on strike. While they are not illegal, they may violate the terms of the collective bargaining agreement.
Working with Labor Unions as Management
First and foremost, when working with labor unions, a clear understanding of the contract is imperative for all managers. The contract (also called the collective bargaining agreement) is the guiding document for all decisions relating to employees. All human resources (HR) professionals and managers should have intimate knowledge of the document and be aware of the components of the contract that can affect dealings with employees. The agreement outlines all requirements of managers and usually outlines how discipline, promotion, and transfers will work.
Because as managers we will be working with members of the union on a daily basis, a positive relationship can not only assist the day-to-day operations but also create an easier bargaining process. Solicitation of input from the union before decisions are made can be one step to creating this positive relationship. Transparent communication is another way to achieve this goal.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- A union has two goals: to add new members and to collect dues. A check-off provision of a contract compels the organization to take union dues out of the paycheck of union members.
- In a union shop, people must join the union within a specified time period after joining the organization. This is illegal in right-to-work states. An agency shop is one where union membership is not required but union dues are still required to be paid. This may also be illegal in right-to-work states.
- Made illegal by the Taft-Hartley Act, a closed shop allows only union members to apply and be hired for a job.
- Collective bargaining is the process of negotiating the contact with union representatives. Collective bargaining, to be legal, must always be done in good faith.
- There are three categories of collective bargaining issues. Mandatory issues might include pay and benefits. Permissive bargaining items may include things such as drug testing or the required equipment the organization must supply to employees. Illegal issues are those things that cannot be discussed, which can include issues that could be considered discriminatory.
- The collective bargaining process can take time. Both parties prepare for the process by gathering information and reviewing the old contract. They then set timelines for the bargaining and reveal their wants and negotiate those wants. A bargaining impasse occurs when members cannot come to an agreement.
- When a bargaining impasse occurs, a strike or lockout of workers can occur. An economic strikeoccurs during negotiations, while an unfair labor practices strike can occur anytime, even during negotiations. A sick-out can also be used, which is when workers call in sick for the day. These strategies can be used to encourage the other side to agree to collective bargaining terms.
- Some tips for working with unions include knowing and following the contract, involving unions in company decisions, and communicating with transparency.
EXERCISES
- Research negotiation techniques, and then list and describe the options. Which do you think would work best when negotiating with unions or management?
- Of the list of bargaining issues, which would be most important to you and why?
11.3 Grievance Process
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
- Be able to explain how a grievance process works.
A grievance procedure or process is normally created within the collective bargaining agreement. The grievance procedure outlines the process by which grievances over contract violations will be handled. As you have probably already identified, the grievance procedure is a formalized conflict, as we discussed in Chapter 9 “Handle Conflict and Negotiation”. Learning how to handle this type of conflict takes self-management skills—or the ability to avoid taking things personally—and relationship management skills. This will be the focus of our next section.
Procedures for Grievances
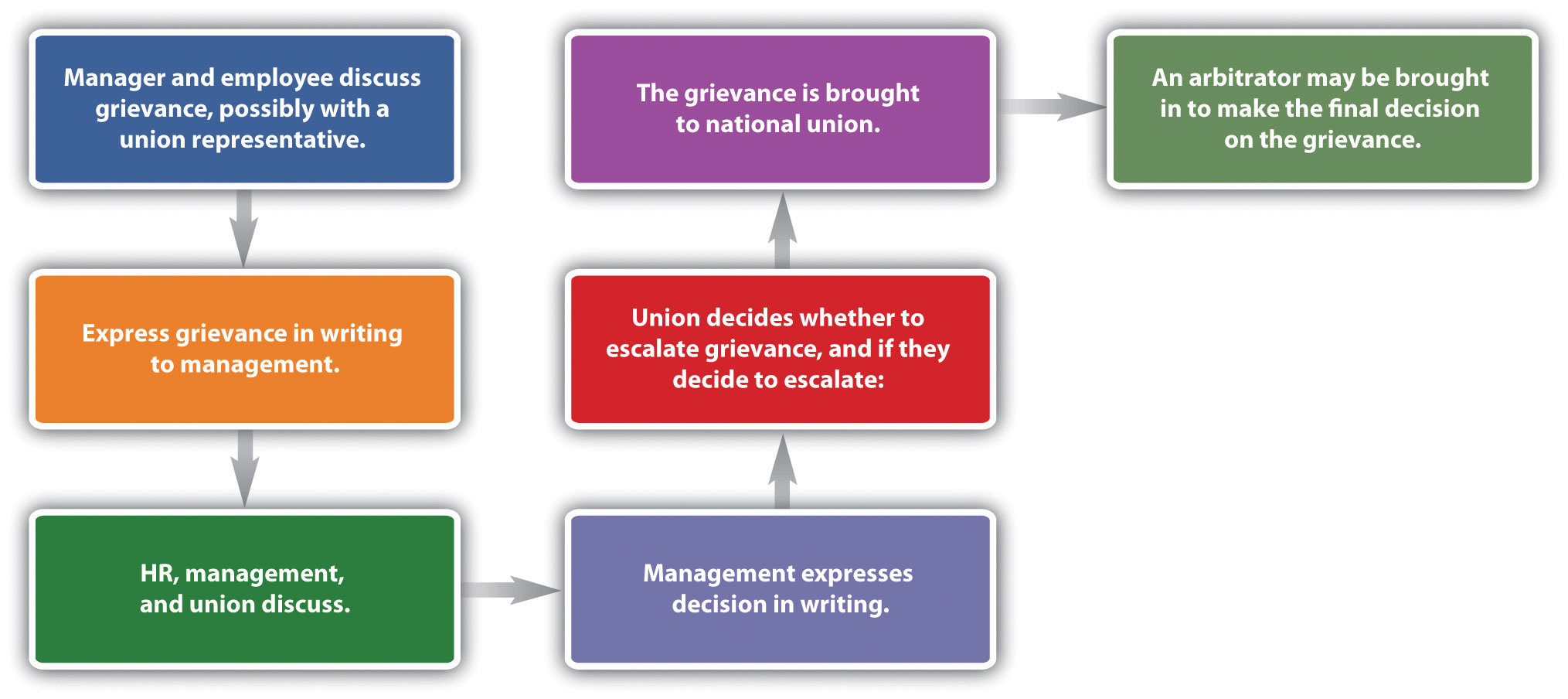
A violation of the contract terms or perception of violation normally results in a grievance. The process is specific to each contract, so we will discuss the process in generalities. A grievance is normally initiated by an employee and then handled by union representatives. Most contracts specify how the grievance is to be initiated, the steps to complete the procedure, and identification of representatives from both sides who will hear the grievance. Normally, the human relations department is involved in most steps of this process. The basic process is shown in Figure 11.8 “A Sample Grievance Process”.
Figure 11.8 A Sample Grievance Process
Why Human Relations?
The discussion of labor unions in this chapter applies to many of the human relations skills we have discussed so far—for example, negotiation, handling conflict, teamwork, and communication. Without these important aspects, effective running of unions would not be possible. Because conflicts happen between union and management, the ability to manage the conflict in a positive way (relationship management emotional intelligence skill) can not only help the negotiations but also help you achieve success with a contract everyone is happy with.
While it pertains to all companies, human relations skills become that much more important to those that have a union environment where management and employees must work together. Conflict in these situations can result in major issues on both sides, such as grievances and strikes. Employing effective human relations skills can reduce conflict and raise productivity in a union environment.
The first step is normally an informal conversation with the manager, employee, and possibly a union representative. Many grievances never go further than this step, because often the complaint is a result of a misunderstanding.
If the complaint is unresolved at this point, the union will normally initiate the grievance process by formally expressing it in writing. At this time, HR and management may discuss the grievance with a union representative. If the result is unsatisfactory to both parties, the complaint may be brought to the company’s union grievance committee. This can be in the form of an informal meeting or a more formal hearing.
After discussion, management will then submit a formalized response to the grievance. It may decide to remedy the grievance or may outline why the complaint does not violate the contract. At this point, the process is escalated.
Further discussion will likely occur, and if management and the union cannot come to an agreement, the dispute will normally be brought to a national union officer, who will work with management to try and resolve the issue. A mediator may be called in, who acts as an impartial third party and tries to resolve the issue. Any recommendation made by the mediator is not binding for either of the parties involved. Mediators can work both on grievance processes and collective bargaining issues. For example, when the National Football League (NFL) and its players failed to reach a collective bargaining agreement, they agreed to try mediation.Associated Press, “NFL, Union Agree to Mediation,” February 17, 2011, accessed August 15, 2011, http://msn.foxsports.com/nfl/story/NFL-players-union-agree-to-mediation-federal-for-labor-talks-CBA-021711. In this case, the agreement to go to mediation was a positive sign after several months of failed negotiations. In the end, the mediation worked, and the NFL players started the 2011–12 season on time. In Washington State (as well as most other states), a nonprofit organization is available to assist in mediations (either grievance or collective bargaining related) and arbitrations. The goal of such an organization is to avoid disruptions to public services and to facilitate the dispute resolution process. In Washington, the organization is called the Public Employment Relations Commission (PERC). Figure 11.9 “The Mediation Process for the Public Employment Relations Commission in Washington State” shows the typical grievance handling process utilizing the free PERC services.
Figure 11.9 The Mediation Process for the Public Employment Relations Commission in Washington State

If no resolution develops, an arbitrator might be asked to review the evidence and make a decision. An arbitrator is an impartial third party who is selected by both parties and who ultimately makes a binding decision in the situation. Thus arbitration is the final aspect of a grievance.
Figure 11.10

Working with a union requires the HR professional to be a good communicator and to view the union-management arrangement as a successful partnership.
© Thinkstock
Some examples of grievances might include the following:
- One employee was promoted over another, even though he had seniority.
- An employee doesn’t have the tools needed to perform his or her job, as outlined in the contract.
- An employee was terminated, although the termination violated the rules of the contract.
- An employee was improperly trained on chemical handling in a department.
Most grievances fall within one of four categories. There are individual/personal grievances, in which one member of the union feels he or she has been mistreated. A group grievance occurs if several union members have been mistreated in the same way. A principle grievance deals with basic contract issues surrounding seniority or pay, for example. If an employee or group is not willing to formally file a grievance, the union may file a union or policy grievance on behalf of that individual or group.
The important things to remember about a grievance are that it should not be taken personally and, if used correctly, can be a fair, clear process to solving problems within the organization.
Grievance Process for Flight Attendants
This video shows a philosophical perspective of the grievance process for the Association of Flight Attendants union.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The grievance process is a formal process to address any complaints about contract violations.
- The grievance process varies from contract to contract. It is an important part of the contract that ensures a fair process for both union members and management.
- HR is normally involved in this process, since it has intimate knowledge of the contract and laws that guide the contract.
- The grievance process can consist of any number of steps. First, the complaint is discussed with the manager, employee, and union representative. If no solution occurs, the grievance is put into writing by the union. Then HR, management, and the union discuss the process, sometimes in the form of a hearing in which both sides are able to express their opinion.
- Management then expresses its decision in writing to the union.
- If the union decides to escalate the grievance, the grievance may be brought to the national union for a decision. At this point, an arbitrator may be brought in, suitable to both parties, to make the final binding decision.
- There are four main types of grievances. First, the individual grievance is filed when one member of the union feels mistreated. A group grievance occurs when several members of the union feel they have been mistreated and file a grievance as a group. A principle grievance may be filed on behalf of the union and is usually based on a larger issue, such as a policy or contract issue. A union or policy grievance may be filed if the employee does not wish to file individually.
- Grievances should not be taken personally and should be considered a fair way in which to solve problems that can come up between the union and management.
EXERCISE
- What are the advantages of a grievance process? What disadvantages do you see with a formalized grievance process?
11.4 Chapter Summary and Case
CHAPTER SUMMARY
- Union membership in the United States has been slowly declining. Today, union membership consists of about 11.9 percent of the workforce, while in 1983 it consisted of 20 percent of the workforce.
- The reasons for decline are varied, depending on who you ask. Some say the moving of jobs overseas is the reason for the decline, while others say unions’ hard-line tactics put them out of favor.
- The United States began its first labor movement in the 1800s. This was a result of low wages, no vacation time, safety issues, and other issues.
- Many labor organizations have disappeared, but the American Federation of Labor (AFL) still exists today, although it merged with the Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) and is now known as the AFL-CIO. It is the largest labor union and represents local labor unions in a variety of industries.
- The United States has a low number of union members compared with other countries. Much of Europe, for example, has over 30 percent of their workforce in labor unions, while in some countries as much as 50 percent of the workforce are members of a labor union.
- Legislation has been created over time to support both labor unions and the companies who have labor unions. The Wagner Act was created to protect employees from retaliation should they join a union. The Taft-Hartley Act was developed to protect companies from unfair labor practices by unions.
- The National Labor Relations Board is the overseeing body for labor unions, and it handles disputes between companies as well as facilitates the process of certifying new labor unions. Its job is to enforce the Wagner and Taft-Hartley acts.
- The Landrum Griffin Act was created in 1959 to combat corruption in labor unions during this time period.
- To form a union, the organizer must have signatures from 30 percent of the employees. If this occurs, the National Labor Relations Board will facilitate a card check to determine whether more than 50 percent of the workforce at that company is in agreement with union representation. If the company does not accept this, then the NLRB holds secret elections to determine if the employees will be unionized.
- A union has two goals: to add new members and to collect dues. The checkoff provision of a contract compels the organization to take union dues out of the paycheck of union members.
- In a union shop, people must join the union within a specified time period of joining the organization. This is illegal in right-to-work states.
- Made illegal by the Taft-Hartley Act, a closed shop allows only union members to apply and be hired for a job.
- Collective bargaining is the process of negotiating the contact with union representatives. Collective bargaining, to be legal, must always be done in good faith.
- There are three categories of collective bargaining issues. Mandatory issues might include pay and benefits. Permissive bargaining items may include things such as drug testing or the required equipment the organization must supply to employees. Illegal issues are those things that cannot be discussed, which can include issues that could be considered discriminatory.
- The collective bargaining process can take time. Both parties prepare for the process by gathering information and reviewing the old contract. They then set timelines for the bargaining and reveal their wants and negotiate those wants. A bargaining impasse occurs when members cannot come to an agreement.
- When a bargaining impasse occurs, a strike or lockout of workers can occur. These are both strategies that can be used to encourage the other side to agree to collective bargaining terms.
- The grievance process is a formal process that addresses any complaints about contract violations.
- The grievance process varies from contract to contract. It is an important part of the contract that ensures a fair process for both union members and management.
- The grievance process can consist of any number of steps. First, the complaint is discussed with the manager, employee, and union representative. If no solution occurs, the grievance is put into writing by the union. Management then expresses its decision in writing to the union. If the union decides to escalate the grievance, the grievance may be brought to the national union for a decision. At this point, an arbitrator may be brought in, suitable to both parties, to make the final binding decision.
- There are four main types of grievances. First, the individual grievance is filed when one member of the union feels mistreated. A group grievance occurs when several members of the union feel they have been mistreated and file a grievance as a group. A principle grievance may be filed on behalf of the union and is usually based on a larger issue, such as a policy or contract issue. A union or policy grievance may be filed if the employee does not wish to file the grievance individually.
- Grievances should not be taken personally and should be considered a fair way in which to solve problems that can come up between the union and management.
CHAPTER CASE
To File or Not?
You work in a large logistics company that is also unionized. Because of the union, your organization has very set pay levels and specific rules for promotion. Recently, your organization has received many big orders and as a result, your manager promoted a fellow employee who did not meet the criteria outlined by the union. You felt you would have been good for the job and are disappointed that you were not selected. You are deciding whether or not to file a grievance.
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of filing a grievance in this situation?
- What type of grievance would this be?
- Explain the process you might go through in order to file a grievance.
- Would you file a grievance or not? Explain your answer.