Business Parks Marketing agency Gamdevi
Fulcrum Marketing is a strategic Business Parks Marketing agency Gamdevi. Our team of marketing consultants also specialise in marketing planning and Business Parks Marketing for all types of business of any size.
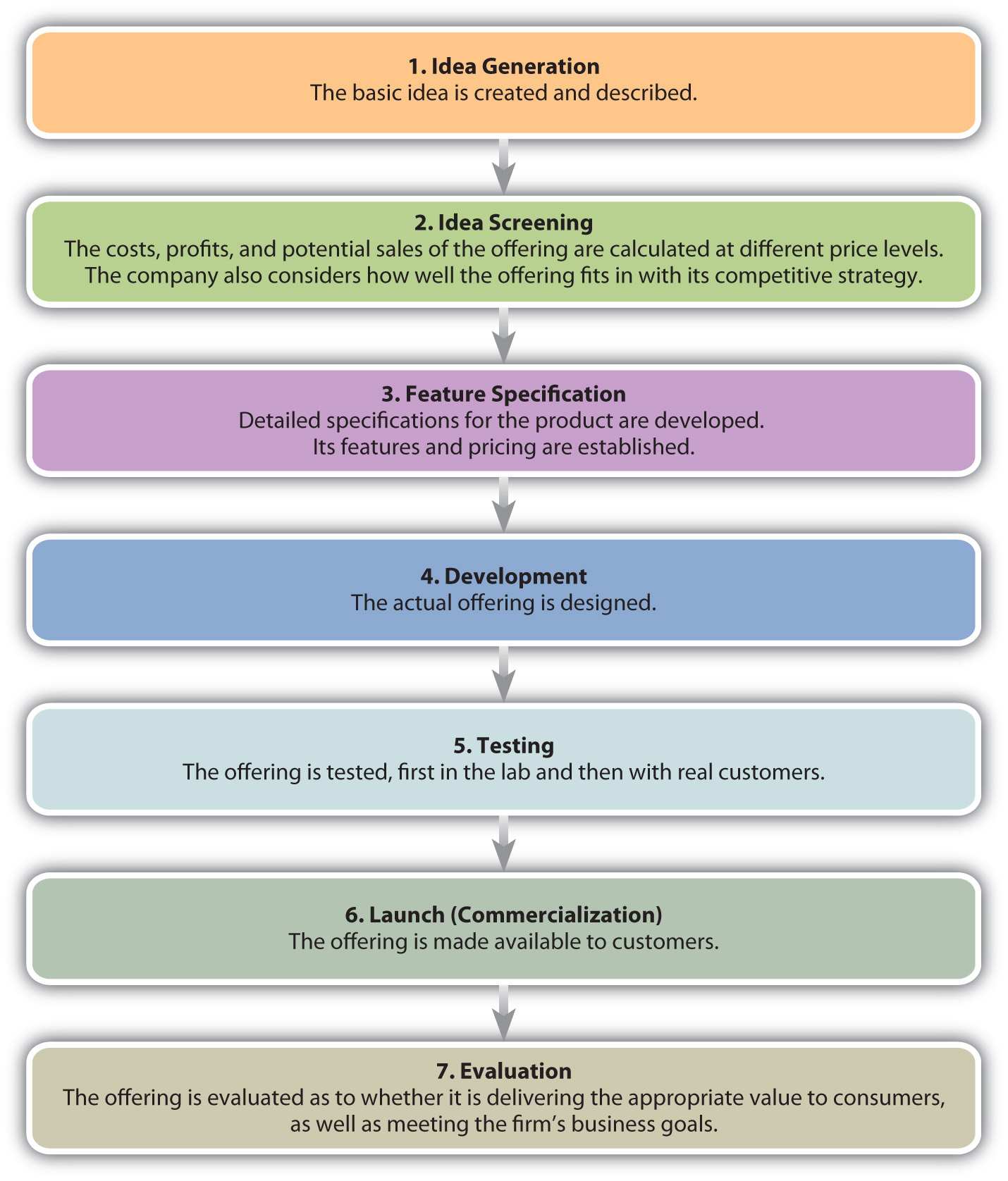
Brand Strategy: Build a Powerful Brand
Your B2B brand determines which signals you’re sending out to the marketplace and how you are perceived by your audience. Whether launching a new service, targeting a niche audience with specific products, or knocking the rust off a dated market position, your brand strategy is fundamental to your company’s success. That’s where we come in. Uncovering the insights that help build an effective, hard-working B2B brand position takes experience — an ability to conduct interviews that deliver more than high-level answers to boilerplate questions; curious researchers willing to explore the idiosyncrasies of your markets; creative minds that bring clarity, even when a compelling position feels obfuscated by internal biases and aggressive competitors.
| Research Interview customers and SMEs Primary, secondary research | Messaging Tell your story convincingly Maintain campaign consistency | Brand Expression Create a visual representation of your brand |
We start with research — talking with your product experts and potential customers to make sure we understand the nuances of your position.
Then, we craft persuasive messages that connect with your target audience, ensuring continuity across all communications.
Finally, we create a visual identity that expresses your brand to a T.
While it’s not quite as easy as one-two-three, we’ll keep it simple, staying focused on the insights that can serve as brand building blocks and avoiding unnecessary trips down rabbit holes that won’t bring any value.
Implementing a Business Parks Marketing Strategy
Implementing a Marketing Strategy Execution Plan, known to Fulcrum and our clients as a “Sprint Plan” is the most effective way to prevent this highway-less journey , Business Parks Marketing agency . A Marketing Strategy is a set of strategic goal-focused plans for a certain period of time.
Business Parks Marketing Strategy and Planning
Implement your marketing plan
Your marketing plan must do more than just say what you want to happen. It must describe each step required to make sure that it happens.
| Schedule The plan should include a schedule of key tasks. This sets out what will be done, and by when. Refer to the schedule as often as possible to avoid losing sight of your objectives under the daily workload. | Team And Resources It should also assess what resources you need. For example, you might need to think about what brochures you need, and whether they need to be available for distribution. You might also need to look at how much time it takes to sell to customers and whether you have enough salespeople. |
| Cost The cost of everything in the plan needs to be included in a budget. If your finances are limited, your plan will need to take that into account. Don’t spread your marketing activities too thinly – it is better to concentrate your resources to make the most of your budget. You may also want to link your marketing budget to your sales forecast. | Control As well as setting out the schedule, the plan needs to say how it will be controlled. You need an individual who takes responsibility for pushing things along. A good schedule and budget should make it easy to monitor progress. When things fall behind schedule, or costs overrun, you need to be ready to do something about it and to adapt your plan accordingly. |
Marketing Execution – Plan, Execute, Track, Measure
Everyone likes to talk about creating a marketing plan. It’s the fun part of marketing, the creative aspect of your planning process and Business Parks Marketing agency . But strategy without execution won’t help your business succeed. In fact, marketing execution is how you achieve results.
Create your marketing strategyDecide how to market your product or service to potential customers by developing a marketing strategy that positions your product to particular customers | Write a marketing execution planHow to identify your objectives and write a plan that will help your marketing generate sales, including tactics and objectives |
Marketing on a tight budgetHow to get the most out of a small or limited marketing budget using cost-effective marketing methods such as Public Relations and online marketing | Marketing your business in PuneHow to market your business effectively in pune including researching your target audience and establishing new contacts |
![]()
Business Parks Marketing,Business Parks Marketing agency GamdeviGet in touch with us, we would love to discuss your marketing needs.We love a good coffee and a challenge, so would behappy to meet up with you face to face.Marketing Company in GamdeviCall Us :-08433772261 | Gamdevi, mumbai |
B2B Marketing:Fulcrum is a magnet for businesses with well-defined goals and a desire to harness the latest advantages that marketing and technology can offer. | Face To Face Marketing :face to face field marketing is also called personal selling or door to door marketing, customers are met directly in order to sell their products, using this method of field marketing. | Product Sampling :Fulcrum are a highly recommended provider of product sampling staff. We specialise in the implementation of sampling campaigns using our in house sampling team and logistical know-how. |
Dealer Marketing:Dealer marketing is of utmost importance for the success of any brand. For most brands, dealers, distributors and resellers are critical links to success. | Direct Marketing:we can help with everything from planning and design to production and delivery ensuring your direct marketing campaigns are delivered on time to the highest quality. | Guerrilla Marketing:When it comes to guerrilla marketing the gloves are off. They are usually low budget campaigns but with the right imagination and ideas they offer up some unprecedented results |
Retail Marketing:Fulcrum is a dynamic-retail marketing agency born in tradition, fueled by innovation, and living at the intersection of commerce and imagination. | Direct Selling :Much like product demonstrations these campaigns have brand reps or ambassadors at the center of them. The difference is it’s more about the selling of the product | Retail Audits & Merchandising: Auditing takes the reps out off the front line and away from the consumer. Auditing teams are used by marketers to monitor traditional marketing strategies that they put in place across retail. |
Door To Door Marketing :Nothing beats the reality that one gets when you can interact with potential clients face to face physically moving from door to door within a community or household to household, | Product Demonstrations:As mentioned already, demo days are a popular tool of field marketing. These campaigns can stretch from as little as one week to 6 months however some are continuous and full time. | Street Marketing:We will still need to spend time interacting with people, face-to-face, Street Marketing. Personal interaction is what makes the world go around |
Business Parks Marketing
Business Parks Marketing agency
The team at Fulcrum has delivering successful Shopping Centre Marketing Campaigns across a wide range of shopping centres and retail complexes. From major retail locations to local community focused shopping centres; we have secured real, measurable results across the board.
Business Parks Marketing Plan and Business Parks Marketing Strategy
Business Parks Marketing agency mumbai
Gamdevi, mumbai
Mumbai, also known as Bombay, is the capital of Maharashtra. It is the most populous city in India and the fourth most populous city in the world. Along with the neighbouring urban areas including Navi Mumbai and Thane, it is one of the most populous urban regions in the world. Mumbai lies on the west coast of India and has a natural harbour.
Seven islands came together to constitute present day Mumbai. During the mid-18th century, Mumbai was reshaped by reclaiming the area between the seven islands from the sea. Bombay was characterized by economic and educational development in the 19th century. Upon India’s independence, the city was incorporated into Bombay State. In 1960, a new state of Maharashtra was created with Bombay as the capital. The city was renamed Mumbai in 1996.
Mumbai is the financial and entertainment capital of India. The city houses important financial institutions such as the Reserve Bank of India, the SEBI, the Bombay Stock Exchange, the National Stock Exchange of India and corporate headquarters of numerous Indian companies and multinational corporations. Mumbai has evolved into a global financial hub.
Mumbai is the financial and entertainment capital of India. The city houses important financial institutions such as the Reserve Bank of India, the SEBI, the Bombay Stock Exchange, the National Stock Exchange of India and corporate headquarters of numerous Indian companies and multinational corporations. Mumbai has evolved into a global financial hub.
It is home to some of India’s premier scientific and nuclear institutes such as BARC, NPCL, AERB, AECI and the Department of Atomic Energy. The city also houses India’s Bollywood movie industry. Mumbai’s business opportunities, as well as its potential to offer a higher standard of living, attract migrants from all over India, making the city a melting pot of many communities and cultures.
In 1950, municipal limits of Bombay were expanded by merging the Bombay Suburban District and Bombay Island City to form Greater Bombay Municipal Corporation (GBMC).
In 1979, a sister township of New Bombay(Navi Mumbai) was founded by the City and Industrial Development Corporation (CIDCO) across Thane and Raigad districts to help decongest and control Bombay’s population.
Textile industry in Mumbai largely disappeared in 1982. Since then, Mumbai’s defunct cotton mills have become the focus of major redevelopment.
Dharavi, Asia’s second largest slum, is located in central Mumbai and houses between 800,000 to one million people in 2.39 sq.km, making it one of the most densely populated areas on Earth.
Key Projects in Mumbai are Omkar Ananta, Xrbia Aashiyana, Oberoi Tata Steel, K Hemani Neona, L&T Emerald Isle, L&T Crescent Bay, Godrej Prime, SPARK DEVELOPERS JYOTI PALACE, BHUMI YUG GARDENS KAMAN, Dosti Codename Landmark, Dosti Vihar, Dosti Planet North, Dosti Imperia Phase I, Mohan Suburbia, Mohan Willows, Piramal Vaikunth, Mohan Palms.
Most searched properties in Mumbai are 1 bhk flats in mumbai, plots in mumbai, villas in mumbai, 2 bhk flats in mumbai, 3 bhk flats in mumbai, house in mumbai, property in thane, property in ulwe, property in panvel, Flats in mumbai.
Key builders in Mumbai are L&T Realty, Lodha Group, Mahindra Lifespaces, Godrej Properties, Paradise Group, House of Hiranandani, Kolte Patil Developers Ltd, Dosti Realty, Lok Group, Mohan Group.
Demographics:
According to the 2011 census, the population of the city is 12,479,608. The city has seen a huge migration of population from all over India in search of employment opportunities. The population density is approximately 20,482 persons per sq.km. The living space is 4.5 sq.mt per person.
According to 2011 census, the sex ratio in the island city is 838 (per 1,000 male) and 857 in the suburbs. Greater Mumbai has a literacy rate of 94.7%. The literacy rate in Mumbai slums is 69% making these slums the most literate slums in India.
Employment Opportunities
Mumbai is India’s most populated city. It is the financial and commercial capital of the country as it generates 6.16% of the total GDP. The city contributes to 10% of factory employment, 25% of industrial output, 33% of income tax collections, 60% of customs duty collections, 20% of central excise tax collections, 40% of India’s foreign trade and 4000 crore in corporate taxes. Mumbai has witnessed an economic boom since the liberalization of 1991, the finance boom in the mid-nineties and the IT, export, services and outsourcing boom in 2000s.
Although Mumbai had prominently figured as the hub of economic activity of India in the 1990s, the Mumbai Metropolitan Region is presently witnessing a reduction in its contribution to India’s GDP.
Many of India’s conglomerates such as Larsen and Toubro, State Bank of India, Life Insurance Corporation of India, Tata Group, Godrej and Reliance, and five of the Fortune Global 500 companies are based in Mumbai.
The key sectors contributing to the city’s economy are gems and jewellery, leather, IT and ITES, textiles, and entertainment. Bandra Kurla Complex (BKC) and Nariman Point are Mumbai’s major financial centres. The Santacruz Electronic Export Processing Zone (SEEPZ) in Andheri and the International Infotech Park (Navi Mumbai) offer excellent facilities to IT companies.
Current situation indicates that the western zone has 33% of the total occupied space in the city implying a large proportion of employment opportunities here. The central zone contributes to 30% of employment.
Connectivity
Mumbai has several major national highways: National Highway 3, National Highway 4, National Highway 8, National Highway 17 and National Highway 222. The Mumbai-Pune Expressway was the first expressway built in India. There are several important highways such as Mumbai Nashik Expressway, Mumbai-Vadodara Expressway, Western Freeway and Eastern Freeway under construction. The Bandra-Worli Sea Link bridge and Mahim Causeway link the island city to the western suburbs. The three major arterial roads of the city are the Eastern Express Highway, the Sion Panvel Expressway and the Western Express Highway.
Mumbai is the headquarters of two of Indian Railways zones: the Central Railway (CR) and the Western Railway (WR). Mumbai is also well connected to most parts of India by the Indian Railways. Long-distance trains originate from Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus, Dadar, Lokmanya Tilak Terminus, Mumbai Central, Bandra Terminus, Andheriand Borivali.
Public transport systems in Mumbai include the Mumbai Suburban Railway, Brihanmumbai Electric Supply and Transport (BEST) buses, taxis, auto rickshaws and ferries. Suburban railway and BEST bus services together accounted for about 88% of the passenger traffic in 2008.
The Mumbai Suburban Railway, popularly known as local trains forms the backbone of Mumbai’s transport system. Mumbai’s suburban rail systems carry more than half of the Indian Railways daily carrying capacity. Trains are overcrowded during peak hours. The Mumbai rail network is spread at an expanse of 319 route kilometres and is growing. The Mumbai Monorail and Mumbai Metro are under construction and expected to be partially operational in 2014, relieving overcrowding on the existing network.
Public buses run by BEST cover almost all parts of the city as well as parts of Navi Mumbai, Mira-Bhayandar and Thane. Maharashtra State Road Transport Corporation (MSRTC) buses provide intercity transport from Mumbai to other major cities of Maharashtra and India. Navi Mumbai Municipal Transport (NMMT) also operates its Volvo buses from Navi Mumbai to Bandra, Dindoshi and Borivali.
The Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport is the busiest airport in India in terms of passenger traffic. An upgrade plan was initiated in 2006, targeted at increasing the capacity of the airport to handle up to 40 million passengers annually. The proposed Navi Mumbai International Airport to be built in the Kopra-Panvel area has been sanctioned by the Indian Government and will help in relieving traffic burden on the existing airport.
Mumbai has two major ports, Mumbai Port Trust and Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust, which lies in Navi Mumbai. Mumbai Port has one of the best natural harbours in the world. Jawaharlal Nehru Port is the busiest and most modern major port in India.
All Localities in Mumbai
LOCALITY, Aarey Road, Agripada, Altamount Road, Amboli, Andheri East, Andheri West, Anushakti Nagar, Azad Nagar, Bandra East, Bandra West, Bangur Nagar, Behram Baug, Bhandup East, Bhandup West, Bhayandar East, Bhayandar West, Bhiwandi, Bhuleshwar, Boisar, Borivali East, Borivali West, Breach Candy, Byculla East, Byculla West, C.P. Tank, Chakala, Chandivali, Charkop, Charni Road, Chembur, Chinchpokli, Chira Bazar, Chuna Bhatti, Church Gate, Colaba, Cuffe Parade, Cumballa Hill, Currey Road, Dadar East, Dadar West, Dahanu Road, Dahisar East, Dahisar West, Deonar, Dharavi, Dombivli West, Dongri, Elphinstone Road, Fort, G T B Nagar, Gamdevi, Gandhi Nagar, Ghatkopar East, Ghatkopar West, Girgaon, Golibar, Goregaon East, Goregaon West, Govandi, Grant Road East, Grant Road West, Haji Ali, J B Nagar, Jacob Circle, Jogeshwari East, Juhu, Juhu Tara Road, Kalbadevi, Kalina, Kandivali East, Kandivali West, Kanjurmarg, Kashimira, Kemps Corner, Khan Abdul Gafar Road, Khar East, LOCALITY, Khar West, Kharodi, Khetwadi, Kurla East, LBS Marg, Lal Baug, Kurla West, Link Road, Linking Road, Lokhandwala, Lower Parel, Mahalaxmi, Senapati Bapat Marg, Malad East, Malad West, Mandapeshwar, Mankhurd, Marine Lines, Marol, Masjid Bunder, Matunga East, Matunga West, Mazgaon, Mira Bhayandar, Mira Road, Mulund East, Mulund West, Mumbai Central, Nahur East, Naigaon East, Naigaon West, Nalasopara East, Nalasopara West, Nariman Point, Navghar Road, Nehru Nagar, Nehru Road, Mandvi, Opera House, Orlem Malad, Oshiwara, Pali Hill, Parel, Peddar Road, Poonam Nagar, Powai, Prabhadevi, Pydhonie, Raigad, S V Road, Sakinaka, Santacruz East, Santacruz West, Sewri, Shastri Nagar, Shivaji Park, Sion East, Sion West, Tardeo, Thakurdwar, Tilak Nagar, Trombay, Tulsiwadi, Vakola, Veera Desai Road, Versova, Vidya Nagari, Vidyavihar, Vijay Nagar, Vikhroli East, Vikhroli West, Vile Parle East, Vile Parle West, Virar East, Virar West, Wadala East, LOCALITY, Wadala West, Walkeshwar, Warden Road, Western Express Highway, Worli, Yari Road, Jogeshwari West, Kalyan West, Karjat, Kasara, Upper Parel, Vasai West, Vasai East, Vikramgad, Mumbai – Nasik Highway, Ambivali, Sahar, Madh, Triveni Nagar, Prabhu Ali, Chinchpada, Bhadane, Neral, Nahur West, Samat Nagar, Sarvodaya Nagar, MHADA Colony, Chedda Nagar, Shivaji Nagar, Beverly Park, Naya Nagar, Govind Nagar, Yogi Jawraj Nagar, IC Colony, Kanti Park, Dindoshi, Evershine Nagar, Chikuwadi, Malvani, Royal Palms, Gokuldam, Narayan Patil Wadi, Upper Worli, Umerkhadi, Nagpada, Ramnagar, Alibag, Gulmohar Road, Murbad Road, Titwala, Khadakpada, Kanakia Road, Saralgoan, Ambernath, Khandas Road, Malabar Hill, Ulhasnagar, Saravali, Palghar, Jawhar, Khandale, Bandra Kurla Complex, Andheri-Kurla Road, Mahavir Nagar, V P ROAD, Kolad, Vitthalwadi, Vasai Road, Carter Road, Murbad, Shahapur, Badlapur East, Ghera Sudhagad, Mahad, Lonere, Roha, LOCALITY, Uttan, Vasai-Nallasopara Link Road, Harihareshwar, Kalyan East, Murbad Karjat Road, Shahad, Badlapur West, Kalher, Dahanu, Bhivpuri, Atgaon, Kalyan-Shil Road, Dombivli East, Gaibi Nagar, Agashi, Thakurli, Navapada, Sir JJ Road, Vangani, Murud, Pali, Gorai, Talasari, Nagothane, Khardi, Kamatghar, Mahim, Khodala, Manori, Antop Hill, Mulund Colony, LBS Marg-Mulund, Kanjurmarg East, Kannamwar Nagar, Panth Nagar, barve Nagar, chirag Nagar, vidyavihar West, vidyavihar East, postal Colony, Jai Ambe Nagar, Sindhi Society, Borla, Ghatla, chembur Colony, Sahakar Nagar, kidwai Nagar, sewri West, Ambernath East, Ambernath West, Manor, Vehloli, Vindhane, Boraj, Umroli, Nagaon, Dohole, Shelu, Sakawar, Gokuldham Colony, Magathane, Ghodbunder, Netaji Nagar, Best Nagar, Kajupada, Dhamote, Kharbao, Anand park, Kopargaon, Matunga, Govandi East, Hariyali, Tungareshwar, Tagore Nagar
|

 (http://www.kraft.com)
(http://www.kraft.com)
